Key Takeaways
- Generative AI gives attackers new powers and lowers the bar to become a malicious actor
- Generative AI can and must also be employed to strengthen cyber defenses
- The need for cybersecurity is greater than ever before and this continues to create investment opportunities
In 2024, the people in 55 countries – who represent 42% of the global population – will vote to elect their leaders, including high-profile elections for the US Presidency and the European Union Parliament1. In addition to attracting billions to cast their ballot, these events are likely to lure malicious actors. With generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools at their disposal, they seek to directly sabotage the electoral process by hacking systems or to sway public opinion using misinformation or deepfakes – their capabilities are greater than ever before.
How is generative AI transforming the cybersecurity battlefield and what might this mean for investors as they postulate what lies ahead for this investment theme?
How generative AI can help attackers
Historically, basic cybersecurity training had been sufficient in enabling people to identify and defend against phishing attacks. Poor grammar, suspicious domains and questionable links were generally easy to spot. However, generative AI tools, like WormGPT2, that are trained on malware-related data and developed specifically for criminal activity can not only eliminate the easy-to-spot giveaways in phishing emails, but they also lower the bar for becoming a malicious actor.
Generative AI can also help polymorphic malware code, a type of program that learns and evolves to automatically become smarter after a failed attempt. This means that if the target does not update its security software, the malware code will come back stronger and exploit any vulnerability in the system3.
Generative AI is also improving the quality of deepfakes. According to the World Economic Forum, between 9 December 2023 and 8 January 2024, 100+ deepfake video advertisements of British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak on Meta were identified, many of which elicited emotional responses, using language such as “people are outraged”4.
Generative AI can also be used for identity theft. If a victim is indeed deceived and discloses their sensitive personal information, then documents like passports and driving licenses can be forged.
How generative AI can help defenders
It is imperative that generative AI is also employed to defend against increasingly sophisticated attacks. For example, generative AI can help develop more advanced training modules to empower users to better guard themselves against high-quality phishing attacks.
Generative AI can also be used to analyse large quantities of data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate vulnerabilities in the system. It can also help cybersecurity teams plug the gaps before a polymorphic malware code makes a return.
Also, generative AI can be used to automate repetitive processes, streamlining tasks that are not only tedious but also prone to human error, like incident response, threat hunting, and malware analysis.
Cybersecurity is more important than ever
The figures below provide an alarming reminder that the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated.
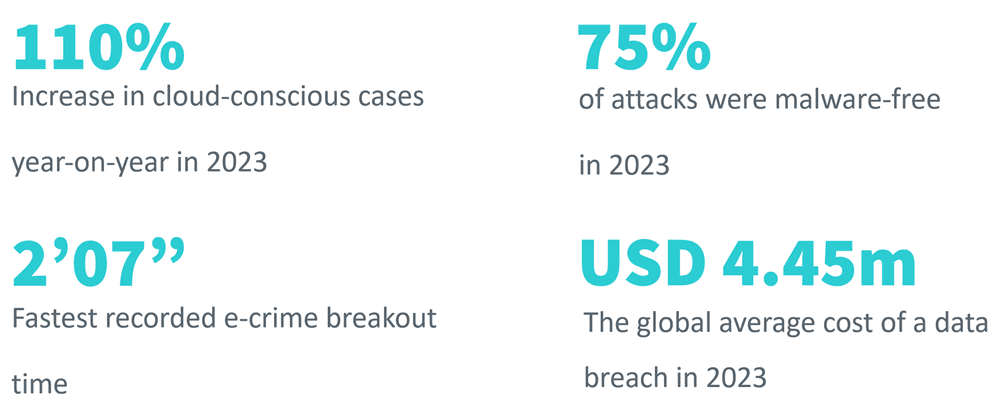
Sources: CrowdStrike, ‘2024 Global Threat Report’, IBM, Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023
Most people who own a smartphone or a laptop typically use dozens of cloud-based software applications. Criminals are recognising this broader attack surface and are increasingly attacking their victims via the cloud. There has also been an alarming increase in sophisticated malware-free attacks: 75% in 2023, up from 40% in 20195. This suggests that attackers are moving to faster and more effective means of infiltrating their target organisations, using means like social engineering rather than always counting on planting malware in their victim’s system. This is an important reminder about how cybersecurity training must not only teach users to defend against phishing attacks but also remain guarded against physical deception.
The e-crime breakout time is how long it takes an attacker to move laterally within an organisation. This means gaining access to other users after initially compromising the first victim. The average e-crime breakout time fell from 84 minutes in 2022 to 62 minutes in 2023, with the fastest recorded time of just over 2 minutes6. And finally, the average cost of data breaches in 2023 to organisations was USD4.45m. This means that attackers are becoming faster, employing a wide range of tools, and causing serious harm to their victims.
Fortunately, organisations are waking up to this reality. According to IBM, 84% of executives plan to prioritise generative AI cybersecurity solutions over conventional cybersecurity solutions in 20247.
What it means for investors
Cybersecurity was among the top-performing themes in 2023. It is, of course, impossible to predict if we will see similar numbers again in 2024. But if the market performance for thematic strategies is a function of strong positive currents in the underlying technologies combined with a broader appreciation of those trends, there is certainly plenty to remain excited about generative AI and its impact on cybersecurity.
Sources
1 Crowdstrike ‘2024 Global Threat Report’
2 https://slashnext.com/blog/wormgpt-the-generative-ai-tool-cybercriminals-are-using-to-launch-business-email-compromise-attacks/
3 https://www.sangfor.com/blog/cybersecurity/what-is-generative-ai-cybersecurity
4 https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/02/4-ways-to-future-proof-against-deepfakes-in-2024-and-beyond/
5 Crowdstrike ‘2024 Global Threat Report’
6 Crowdstrike ‘2024 Global Threat Report’
7 https://www.ibm.com/thought-leadership/institute-business-value/en-us/report/ceo-generative-ai/cybersecurity
8 Source: Bloomberg, based on net total return indices.
©2023 WisdomTree Digital Movement, Inc.







